Importance of Carbohydrates in Human Diet
The Importance of Carbohydrates in the Human Diet
Abstract:
Carbohydrates, often referred to as the body’s primary source of energy, play a crucial role in maintaining human health and well-being. This essay explores the significance of carbohydrates in the diet, discussing their various forms, functions, and effects on the body. From simple sugars to complex starches, carbohydrates contribute to energy production, brain function, and overall metabolic balance. This article also addresses common misconceptions about carbohydrates and provides insight into their role within a balanced diet.
Essay:
Carbohydrates are fundamental macronutrients that serve as a primary source of energy for the human body. Comprising a diverse array of compounds, carbohydrates are found in various foods and play a vital role in maintaining overall health and functionality. This essay delves into the importance of carbohydrates in the human diet, exploring their forms, functions, and impact on well-being.
List of Topics:
Introduction to Carbohydrates and their Classification
The Role of Carbohydrates in Energy Production
Simple Sugars: Fuel for Immediate Energy
Complex Carbohydrates: Sustaining Vitality
Carbohydrates and Brain Function
The Connection Between Carbohydrates and Insulin
Dietary Fiber: Promoting Digestive Health
Misconceptions About Carbohydrates and Weight Gain
Carbohydrates in Athletes’ Diets: Performance and Recovery
Balancing Carbohydrate Intake within a Healthy Diet
The Role of Carbohydrates in Energy Production
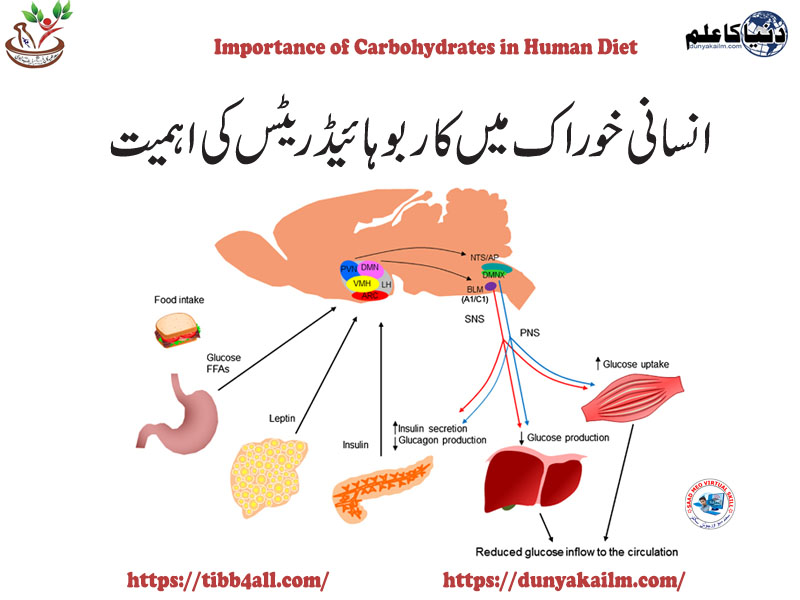
Carbohydrates are the body’s preferred energy source, providing the fuel needed for everyday activities and bodily functions. Simple sugars, such as glucose and fructose, are rapidly absorbed, providing quick bursts of energy. Complex carbohydrates, on the other hand, release energy gradually, sustaining the body’s vitality over a more extended period.
Carbohydrates and Brain Function

The brain heavily relies on glucose as its primary energy source. Carbohydrates help maintain cognitive function, memory retention, and concentration. A diet lacking in carbohydrates may lead to fatigue, decreased mental acuity, and impaired decision-making.
Carbohydrates and Insulin

Carbohydrates play a crucial role in regulating blood sugar levels. Upon consumption, carbohydrates are broken down into glucose, causing a rise in blood sugar. The hormone insulin helps transport glucose into cells, where it is either used for energy or stored as glycogen in the liver and muscles.
Dietary Fiber: Promoting Digestive Health
Dietary fiber, a type of carbohydrate, aids in maintaining a healthy digestive system. Fiber adds bulk to stool, facilitating regular bowel movements and preventing constipation. Additionally, it helps control appetite and promotes a feeling of fullness.
Misconceptions About Carbohydrates and Weight Gain
Carbohydrates have often been unfairly blamed for weight gain. While excess calorie intake from any macronutrient can lead to weight gain, it’s essential to recognize the difference between nutrient-dense carbohydrates and highly processed, sugary foods. Whole grains, fruits, and vegetables offer vital nutrients and should be included in a balanced diet.
Carbohydrates in Athletes’ Diets

For athletes, carbohydrates are especially crucial. They provide the energy needed for high-intensity workouts and aid in post-exercise recovery. Carbohydrate-rich meals before and after exercise help replenish glycogen stores and optimize performance.
Balancing Carbohydrate Intake
Balancing carbohydrate intake is vital for overall health. While carbohydrates are essential, excessive consumption of refined sugars and processed foods can contribute to health issues such as obesity and type 2 diabetes. Opting for whole, unprocessed foods and monitoring portion sizes are key to maintaining a balanced carbohydrate intake.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Are all carbohydrates the same?
How do carbohydrates affect blood sugar levels?
Can a low-carb diet be beneficial for weight loss?
What are the best sources of dietary fiber?
How do carbohydrates impact diabetes management?
Is it necessary to consume carbohydrates before exercise?
What role do carbohydrates play in children’s diets?
Are there “good” and “bad” carbohydrates?
How can one strike a balance between carbohydrates and other nutrients?
Can carbohydrates be consumed in the evening without negative effects?
Conclusion:
Carbohydrates form the backbone of a healthy and balanced diet. From supplying energy to supporting brain function and digestive health, these macronutrients are indispensable to human well-being. It is crucial to recognize the various forms of carbohydrates and their effects on the body, debunking common misconceptions and making informed dietary choices. By incorporating a variety of nutrient-dense carbohydrates into our meals and practicing moderation, we can harness the benefits of carbohydrates while promoting optimal health and vitality.