Importance and usefulness of water content in the human body
Importance and usefulness of water content in human body list box
Introduction
Importance of water in human physiology
Body water regulation
Factors Affecting Body Water Percentage
Understanding water content measurements
Clinical methods for determining body water
Bioelectrical impedance analysis for hydration assessment
Implications of body water imbalance
Frequently Asked Questions
Result
-
Introduction
When we examine the complex workings of the human body, we encounter an essential element that sustains life in all its forms – water. This clear, tasteless substance is an important part of our body’s structure, serving as the basic building block for various bodily processes. The importance of water within the human body cannot be overstated, and this article aims to shed light on the fascinating realm of body water content.
-
Importance of water in human physiology

Water is not just a basic need. It plays an important role in supporting life. Cells within the human body are primarily composed of water, making it an essential structural component. Additionally, water facilitates extracellular communication, molecular transport, and biochemical reactions such as hydrolysis.
Water is not just a mundane liquid. It is the life blood that flows through our biological vessels. Within the confines of each cell, water dominates the cytoplasm, which forms the basis of cellular structure. Beyond its intracellular role, water acts as a medium for communication between cells, facilitating the complex dance of molecular transport throughout the body. Additionally, water takes center stage in important biochemical reactions, such as hydrolysis, which breaks down molecules into smaller components necessary for bodily functions.
-
Regulation of body water
The complex balance of body water is a symphony orchestrated by the renal and neuroendocrine systems. This balance is important for maintaining blood pressure and cardiac output, key players in overall homeostasis. Hormones such as antidiuretic hormone (ADH), renin, angiotensin II, aldosterone, and atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) act as messengers, coordinating the regulation of body water intake. These chemical signals pass between the kidneys and the hypothalamus, while other organs such as the lungs and heart are also involved in the course, releasing hormones such as angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) and ANP.
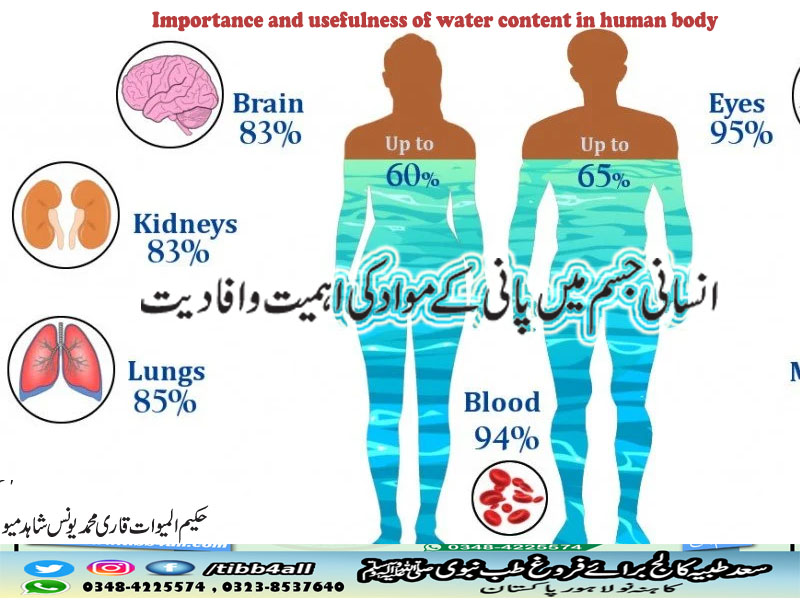
Amount of water essence
- Factors affecting body water percentage
Measuring the water content of the body is a complex endeavor. The human body, on average, is about 57% water, a ratio that fluctuates throughout life. For example, in newborns, water can make up 79 percent of body weight, but this proportion decreases with age. Even obesity has an effect, potentially reducing water intake by as much as 45 percent. These ratios, coupled with the fluid fractions dispersed within various body cavities and tissues, can offer valuable insight into the state of health or disease.
.
- Understanding the measurement of water content
Determining the amount of water in the body is very important for assessing health and diagnosing conditions
Methods for determining body water content range from elementary to sophisticated. Calculations based on body weight and urine output provide a rough estimate, albeit with some degree of uncertainty. Meanwhile, modern techniques, such as mass spectrometry, use the principles of dilution and equilibrium to measure the abundance of water in breath samples. Bioelectrical impedance analysis offers another approach, using accurate measurements of electrical resistance within body tissues to assess hydration levels. The higher the resistance, the lower the hydration – a clear manifestation of the conductive nature of water
- Clinical methods for determining body water

There are various clinical methods for estimating body water, ranging from simple calculations based on body weight and urine output to more sophisticated techniques such as dilution and equilibration using mass spectrometry. These methods help identify deviations from normal hydration levels.
-
Bioelectrical impedance analysis for hydration assessment
Bioelectrical impedance analysis is a widely used technique for assessing body composition and hydration levels. By measuring resistance to electrical flow through body tissue, this method provides valuable information about an individual’s hydration status and overall health.
-
Implications of body water imbalance

An imbalance in the amount of water in the body can have significant health implications. Dehydration can lead to fatigue, impaired cognitive function, and even life-threatening conditions in severe cases. Conversely, excess fluid retention can indicate underlying health problems such as heart or kidney problems.
- Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: How does obesity affect body water percentage?
Q2: Are there any natural ways to improve hydration?
Q3: Can body water imbalance affect athletic performance?
Q4: What role does water play in biochemical reactions?
Q5: How does aging affect water distribution in the body?
- Conclusion
Water is much more than a simple drink. This is a basic element